The post Can Cats Be Sexually Attracted to Humans? Dispelling the Myths (Vet-Verified) by Chris Dinesen Rogers appeared first on Catster. Copying over entire articles infringes on copyright laws. You may not be aware of it, but all of these articles were assigned, contracted and paid for, so they aren't considered public domain. However, we appreciate that you like the article and would love it if you continued sharing just the first paragraph of an article, then linking out to the rest of the piece on Catster.com.
Click to Skip Ahead
Our relationship with our animal companions has evolved through the ages. When we once considered cats to be mere mousers, we’ve since invited them into our homes and lives. Perhaps this relationship was destined to be since we share 90% of our DNA with felines.1 They’ve even changed their vocal repertoire to include meows not typically heard in their wild counterparts.
Evidence of vocal and emotional recognition exists.2 However, there’s nothing sexual about a cat’s affection for their caregivers. Humans provide a sense of comfort to their pets that they recognize. After all, they depend on us for food, water, and shelter. Still, that doesn’t mean they’re sexually attracted to us.

The Human-Cat Bond
Research suggests the Ancient Egyptians changed our relationship with cats, with evidence pointing to them having a place in the home alongside humans.3 However, we’re still talking about an owner-pet or bond and not a sexual one. Undoubtedly, their role as mousers in Ancient Egypt still existed the same as it did when they were first domesticated, but the difference was probably the building of affection between people and cats.
Feline Reproductive Behavior
Of course, humans associate sexual attraction with reproduction. That’s where we find the strongest evidence that cats are not attracted to people in that way. Our pets are quite in touch with their wild roots. Domestication has changed only 13 genes in cats, which translates into a feline breeding season between mid-January and mid-October, triggered by longer daylight hours.4 This is likely related to producing young when there is lots of food available. Cats living inside can cycle at all times of the year due to exposure to artificial light.
Females undergo estrus or heat cycles every 21 days, on average. During this time, cats yowl to attract potential mates, while the males search for receptive females. Bonding doesn’t exist since they are polygynandrous, meaning females and males have multiple mating partners. Another biological factor is that felines have induced ovulation. The mating act triggers ovulation so the female has a high chance of pregnancy.
The cat embodies the theory that mating and reproduction have only a biological purpose. Males provide no parental investment in the offspring or love for the female after mating has occurred. Rearing of the young is done solely by the mother. The animal’s mating system is living proof of that assertion. Pair bonding in felines is not the usual sexual relationship between adult cats.
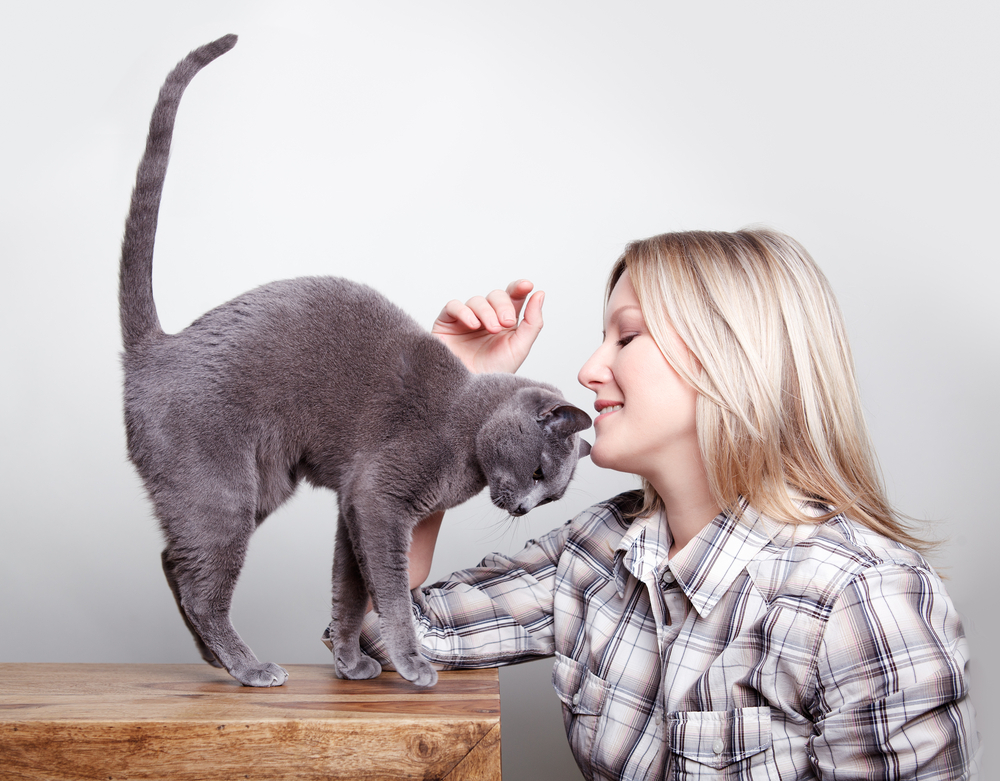

Signs of Affection
Cats that are attached to their caregivers are often quite expressive. They may rub against your legs or give you head-butts. They may purr as you hold them or knead you. Interestingly, some of these behaviors are identical to those between the mother and kittens. They point to the love and affection that exists in these relationships.
You may wonder what your cat really thinks about you. We can make some inferences based on feline body language. When your kitty rubs against your leg, they are showing affection. This behavior is believed to be scent-marking the human as a member of their colony.
The fact that your pet has this physical contact with you is evidence of their affection. After all, they wouldn’t engage with another animal if they didn’t think they were friendly. Again, it’s not sexual but an acknowledgment of their attachment.
The Role of Oxytocin
Research into the hormone oxytocin provides additional insights. The body releases this chemical compound during pleasurable interactions often involving trust and the intimacy of maternal care. It can also reduce circulating stress hormones in humans and non-humans. While oxytocin is also associated with sex, it has an equivalent role in non-sexual affection.
While the research is limited, one study found that human-animal interactions can increase oxytocin release in dogs and humans. And, another study found that humans can release oxytocin when interacting with cats. It’s not a stretch to hypothesize the same effects can occur with cats. Scientists have already found that felines can be just as effective as canines for therapy animals. The action of oxytocin may explain the mechanism for how it happens and refine our understanding of how cats show affection.
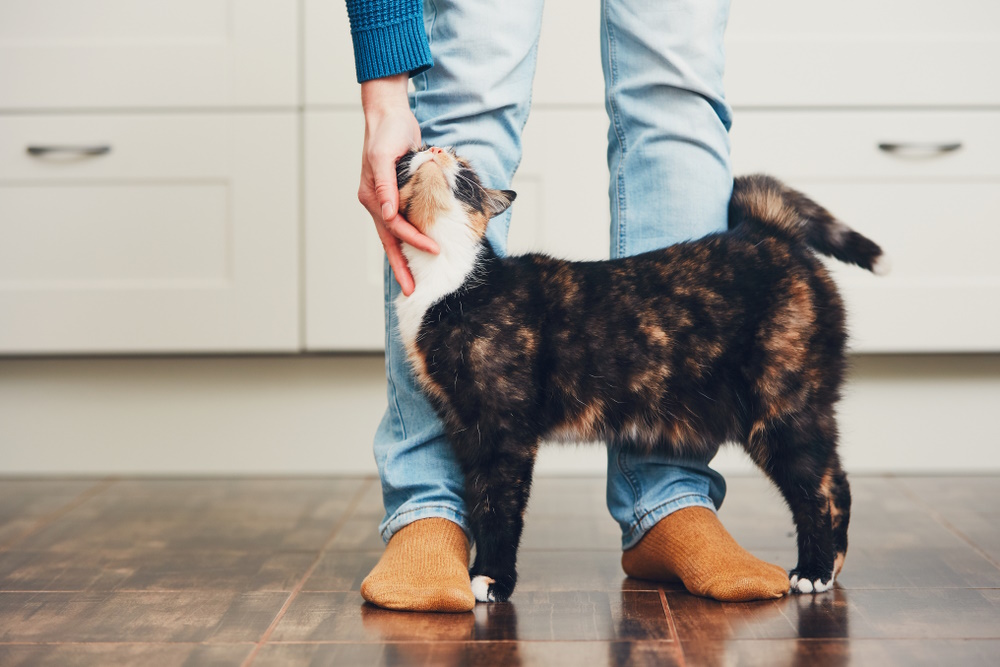


Final Thoughts
Science has shed new light on cats and their behavior. Research proves ample evidence that felines bond with their owners and express it physically and vocally. However, sexual attraction is not a part of that mix, nor is it with mating. For cats, mating occurs for the biological purpose of making kittens and they usually do not form strong bonds with a mating partner. Nevertheless, affection and love are part of our lexicon to describe our relationship with our pets.
Featured Image Credit: larisa Stefanjuk, Shutterstock
The post Can Cats Be Sexually Attracted to Humans? Dispelling the Myths (Vet-Verified) by Chris Dinesen Rogers appeared first on Catster. Copying over entire articles infringes on copyright laws. You may not be aware of it, but all of these articles were assigned, contracted and paid for, so they aren't considered public domain. However, we appreciate that you like the article and would love it if you continued sharing just the first paragraph of an article, then linking out to the rest of the piece on Catster.com.
from Catster https://ift.tt/PMnwVKt
